Since dmm was developed during the time period when vinyl was being overtaken by cassette tapes and ultimately compact discs as the dominant consumer music formats use and r d work was not extensively implemented in the.
Cut lacquers vinyl.
I think this is going off on a dangerous tangent if left unchecked.
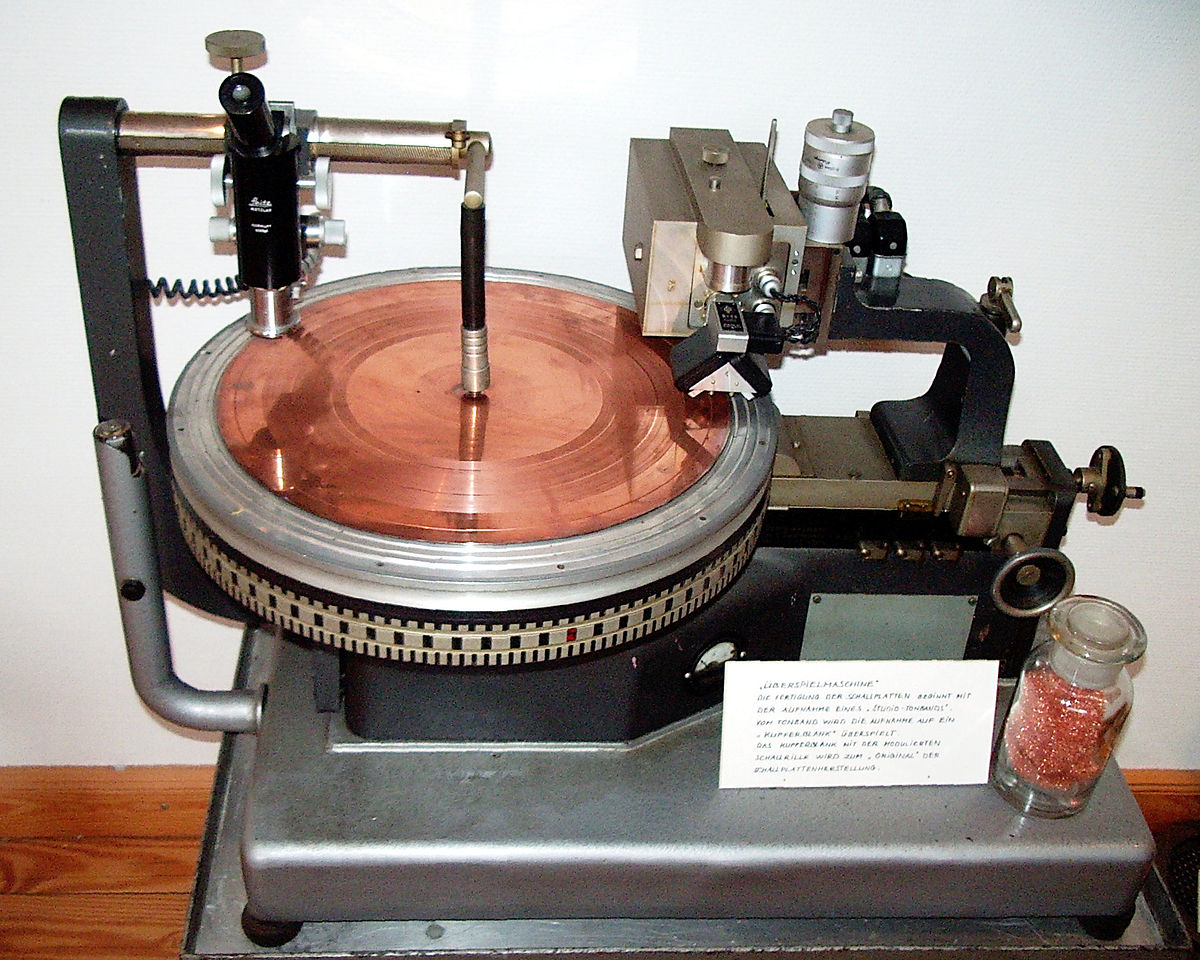
Instead of cutting into a blank lacquer grooves are cut into a blank copper disc via a specially equipped lathe.
Although not comparable in scale frank remembers the dubplate scene as offering creative precedent for the current situation.
If the cutting engineer is not the dude at the plant who just pounded three beers on his friday lunch break but rather a sober and experienced cutting engineer working in a sterile environment on a well maintained lathe there is hope of a properly cut lacquer.
Once the music has been mastered the lacquer cutting can begin.
There s a company called vinyl recorder that developed a lathe to cut into plastic and cutting into plastic rather than acetate or lacquer meant that the discs lasted much longer into the thousands of plays.
Direct metal mastering dmm.
This is a technology developed in the mid 1980 s for cutting masters for record manufacturing.
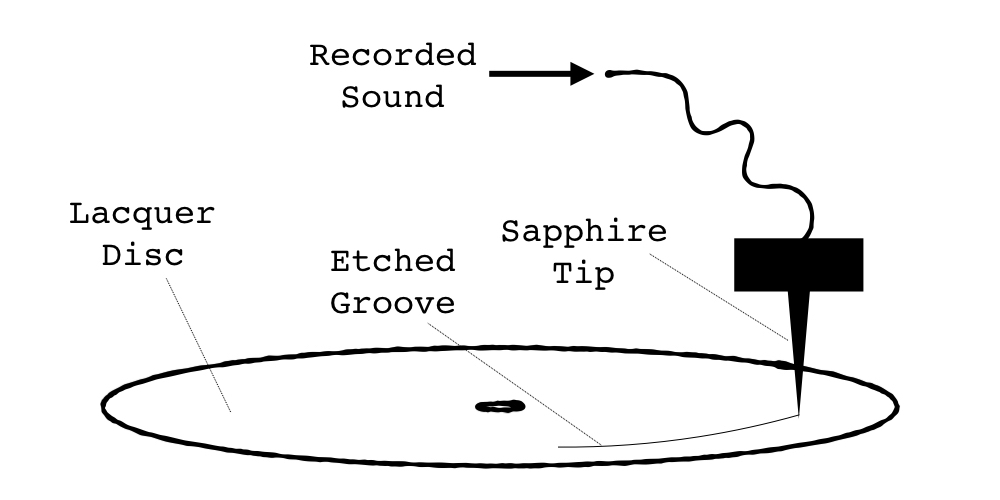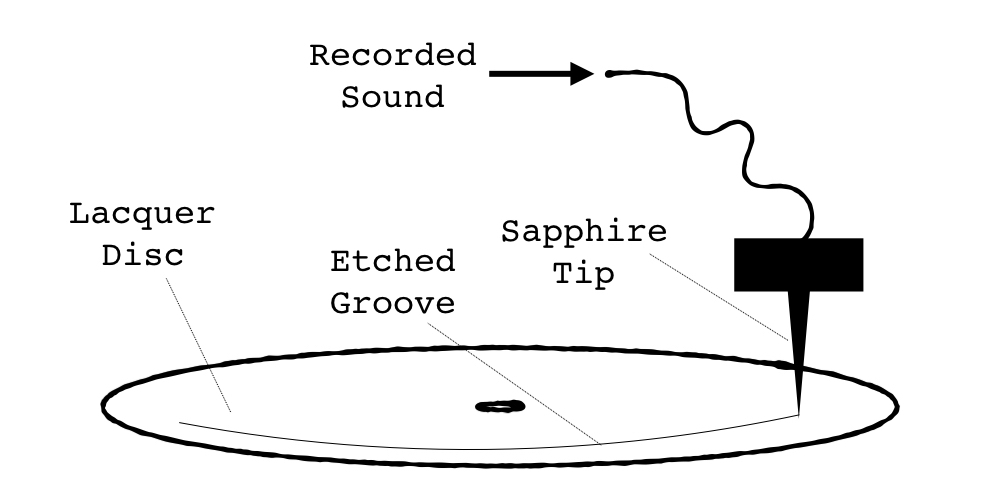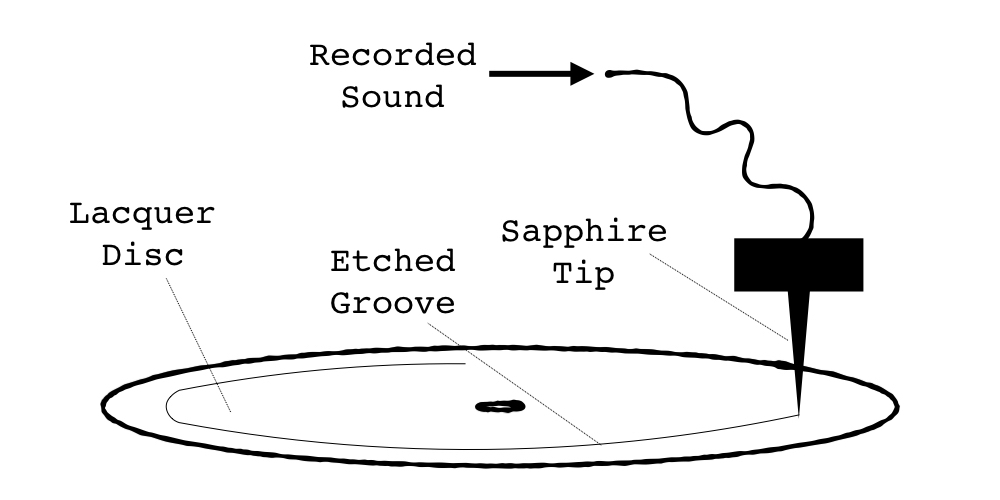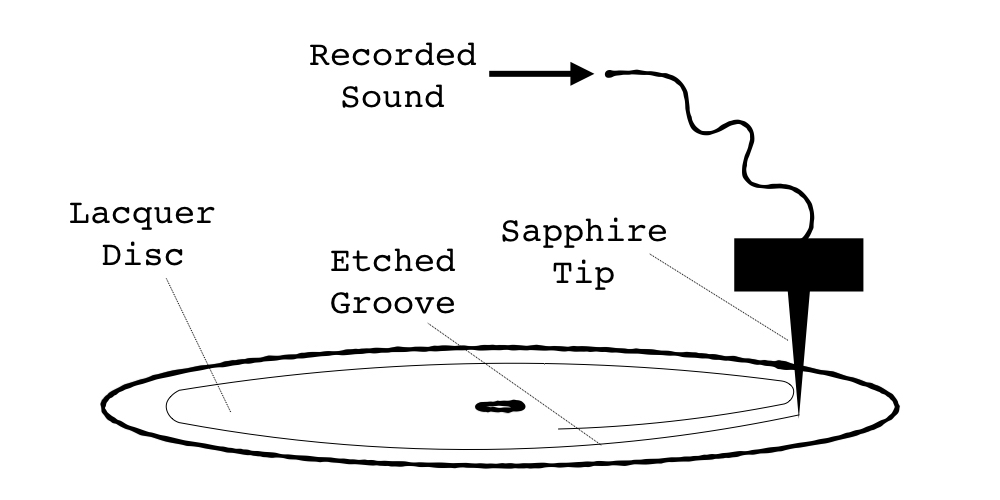
This stage involves audio engineers using a lathe machine and a very sharp gemstone to carve your music onto a flat lacquer coated metal disc.
Unlike ordinary vinyl records which are quickly formed from lumps of plastic by a mass production molding process an acetate disc is created by using a recording lathe to cut an audio signal modulated groove into the surface of a special lacquer coated blank disc a real time.
This is crucial for the vinyl s final quality since the lacquer errors amplify themselves during the process of galvanization of stampers for pvc moulding.
Sending your audio straight to a vinyl pressing plant and letting them handle the lacquer cutting is essentially the equivalent of that.
Theoretically both sides of a lacquer could be used for cutting.
This is the first and most delicate step in the record making process.
See also lacquers and lathe.
The cutting engineer plays the stereo tracks and uses a lathe to cut grooves into a blank lacquer disc.
Transferring your digital vinyl pre master to a lacquer is an extremely crucial process and has a major influence on how your vinyl will sound.
Vinyl mastering and lacquer disc cutting vinyl mastering consists of optimizing the final mastered song for the unique characteristics of the vinyl format which include low and high frequency treatment level adjustment groove spacing optimization and if necessary low end summing to eliminate undesirable phasing that can occur from stereo effects in the bass frequencies on vinyl.
However the manufacturer guarantees a flawless surface for only one side of the lacquer.
Acetate discs are used for the production of vinyl records.
Lacquer technology cutting into lacquers is an older method of mastering for vinyl records but still has many supporters and fans.
Lacquers are often cut by those who have made the vinyl master and all that is on the release is the mastering engineer s handle initial.
This analogue mastering technique is widely accepted and used thanks to bigger number of lacquer cutting lathes available and the tradition of lacquer mastering through the years.